With another year of innovation behind us, we’re excited to think about the possibilities that 2023 holds for live broadcast production. As the media industry forges on, we know more efficient ways of working will transform live video. But, before we dive into our predictions for the coming year, let’s first take a look at all that happened in 2022.
2022 at Haivision
Last year was a particularly momentous one for Haivision as we acquired Aviwest, bringing not only cutting-edge mobile contribution technology but also industry-leading expertise into the Haivision family. The complementary products this acquisition added to the Haivision live broadcast solution portfolio allows us to respond to our customers’ growing demand for high-quality live video content in broadcast, sports, and live event production. Our mobile video contribution products, built under the same philosophy of innovation and reliability, are an answer to the direction of the industry and increasing adoption of 5G and bonded cellular systems.
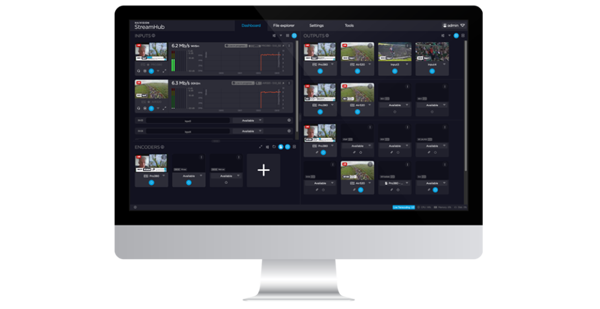
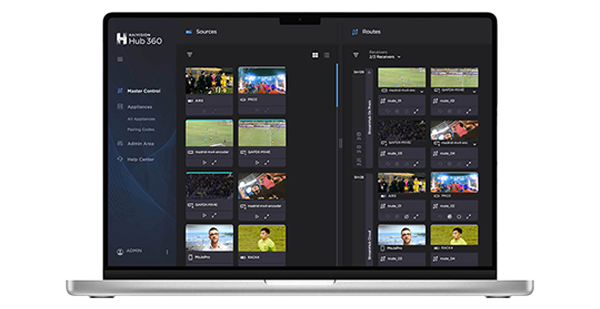
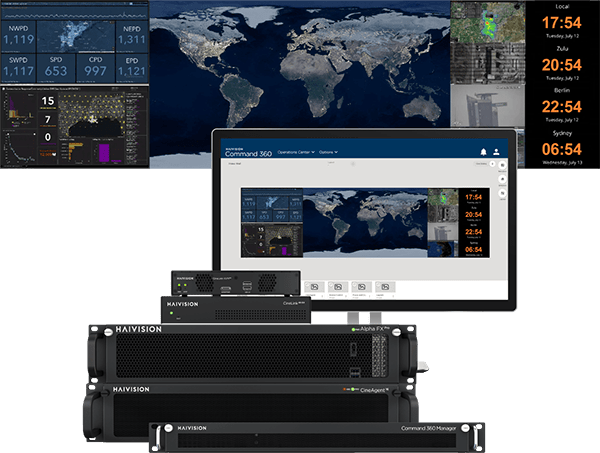
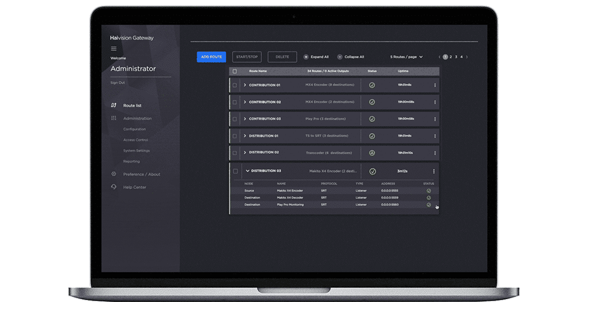
In addition, Haivision Command 360 and Haivision Hub MCR were unveiled, offering two distinct solutions to support critical operations for completely different markets.
But enough about us! Let’s talk about some upcoming trends that we can expect to see in 2023.
What’s Ahead for Live Broadcast Production in 2023
5G + Dedicated Network Slicing
We’d be remiss in talking about the future if we didn’t put a spotlight on 5G innovation.
5G has moved beyond Proof of Concept (PoC) as of 2022 and, as a result of this, will continue to gain momentum in its adoption by more broadcasters for remote and live video production. In the coming year, we’ll see a decrease – albeit gradual – in the upfront cost to implement this next-generation infrastructure. In tandem with this, CSPs will start to offer network slicing for broadcasters.
As 5G becomes more widely available, dedicated network slices will become an attractive option for broadcasters as network slicing can achieve quality-of-service (QoS) and, in doing so, add a layer of reliability that makes it a feasible option for live video broadcast. Private 5G networks can also replace cables and WiFi, expanding broadcasters’ capabilities in the field. While new technologies can be adapted to bridge the gap from old services to new when deploying these new 5G systems, it adds another cost to 5G rollout, to which we can attribute some reluctance to make the shift.
Remote Production (REMI) + Hybrid Work
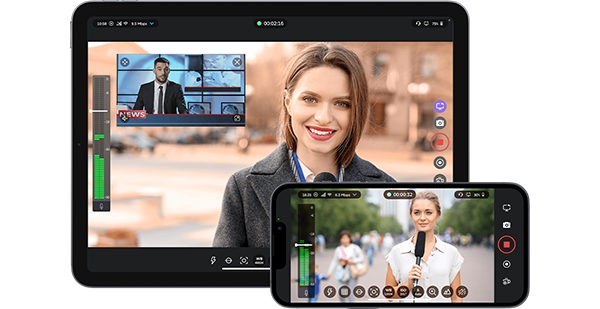
Speaking of 5G, we expect to see continued growth in remote production that leverages this next-gen technology, as well as further innovation in live video contribution over mobile networks – especially as 5G continues to be deployed more pervasively around the world. This means an increased use of bonded cellular and 5G technology in the remote production mix for more broadcasters. IP-based production extends broadcasters’ ability to use a range of protocols to capture signals from multiple inputs. Among the most attractive benefits of this are streamlined costs and the ability to transmit 4K UHD content.
As the hybrid way of working remotely continues to be reinforced, remote collaboration has become the new normal. Not only that, but remote production (or REMI) offers flexibility in choosing talent, allowing broadcasters the ability to leverage talent across traditionally limiting geographical bounds. In 2023 we will see more broadcasters make long-term plans and investments into more flexible workflows to support ongoing remote collaboration.
A Shift in Live Sports + OTT Streaming
While it was typical for first-tier sporting events to be broadcast live before the pandemic, the growing demand for live streaming over the Internet and mobile networks will affect second- and third-tier events much more profoundly. These events can be covered more widely if companies adopt remote production models and transition away from exclusive use of OB van productions.
This, coupled with our knowledge of 5G innovation, means that it wouldn’t be all that surprising to see stadiums adopt next-generation technology such as 5G to deliver this experience, especially when it boasts benefits that reduce the need for cables, legacy wireless RF technology, and WiFi.
This is relevant to OTT streaming as well; as more broadcasters produce 4K content, OTT streaming distributors will have more cause to deliver live 4K and HDR content to consumers. As with any state of transition, many broadcasters (in live sports, for example) will have to produce content for both traditional broadcasting methods (such as satellite) and for OTT streaming. In this instance, cloud offers flexibility to accommodate live broadcast production for various streaming destinations.
Specifically in live sports, we anticipate 2023 to see major transitions to systems using bonded cellular and 5G, cloud, and remote production technologies, all of which lead to more agile broadcast production models. Cloud-based production in particular is on track to become commonplace in live broadcast, largely in part due to benefits like cost-efficiency and the ability to leverage production talent without being restricted by the necessity of being in-person.
2022 set the stage for some exciting developments in this coming year (and beyond). Between 5G network slicing, remote production models, and new standards set for live sports broadcast production, the media and entertainment industry is poised for continued innovation in 2023.