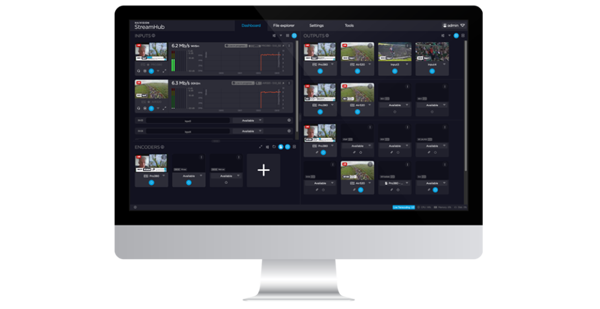
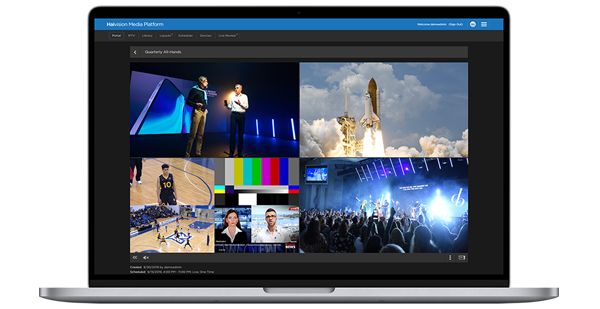
Keeping workers informed and up to date has always been a vital part of an organization’s success and with some of the workforce unable to physically meet for presentations and all-hands meetings, this has presented new challenges to face. Thankfully, organizations can leverage scalable video streaming technologies such as Haivision Media Platform with complete eCDN functionality to adapt to these emerging virtual enterprise work environments and overcome new corporate communication challenges.
This post looks at what an eCDN is, what it’s used for, some of the different types of eCDNs that are available, and how adopting one can help with these new virtual enterprise workflows.
What is an eCDN and how is it Different From a CDN?
To understand what an eCDN is and does, we should first look at what a CDN is. A CDN, or a content delivery network, is a global network of servers and data centers for temporarily storing (caching), delivering, and distributing both live and on-demand (VOD) content to local servers, or edge servers, that are located as close to the viewer as possible. Instead of everyone accessing a single origin server at the same time from all over the world, the video content is distributed to local regions before being forwarded on to individual viewing devices.
An eCDN, or enterprise content delivery network, serves the same function as a CDN which is used by consumer video streaming services, but instead leverages an organization’s own private networks, such as LANs and WANs, to securely distribute content to employees and authorized viewers.
Besides the use of private networks, the main difference between the two is that an eCDN is typically used by an organization for internal use, while a CDN is used by a content creator or owner to publicly distribute their content over the internet.
Three Types of eCDN Technologies
There are three important types of eCDN technology, each with their own use cases and advantages. However, this doesn’t mean that multiple types eCDNs can’t be used simultaneously to optimize content delivery.
Multicast or IPTV: When on shared local area networks (LAN), users can all view a single video stream. A local eCDN server, which may be caching a stream from a remote origin server, can deliver all the packets that make up a video stream to all local users. This results in a reduction of bandwidth usage as only one video stream needs to be shared. Multicast is typically for sharing live events or rebroadcasting live television content throughout a facility network and is sometimes referred to as IPTV.
Caching: Caching stores videos close to the end user’s location on a network, whether it’s a private LAN or the Internet. When a viewer requests a certain video for the first time, the cache retrieves it from the source, or origin server, and stores a copy of it locally. When other users request the same video content, it can then be sent from the local cache and not the central origin server resulting in less network congestion and better-quality video. eCDN caching can be used for VOD content as well as for live events.
P2P (peer-to-peer): A P2P eCDN helps overcome network congestion created by multiple users, or peers, in the same space watching the same content. By creating connections between the devices being used by the end users who are streaming the same video, the content is cached on individual computers and set-top-boxes so that the video content can be shared among them in high quality and with a reduced amount of congestion.
What are the Key Advantages of Using an eCDN?
Some of the challenges faced by organizations when it comes to content delivery include network congestion which leads to a bottleneck in bandwidth, poor video quality, persistent buffering, and delays in starting up. With an eCDN, organizations are provided with more control and visibility of their content as the proxy and cache servers are all located internally within their own WAN or LAN or dedicated datacenter. Even more important is the level of security that an eCDN provides including firewall settings, watermarking, AES encryption, and more. With the use of these private networks and robust security measures, an organization’s proprietary content can be delivered securely and quicky to only those that need to see it.
Another advantage to using an eCDN is that it saves on costs by cutting down on excessive bandwidth consumption. An eCDN is also easily deployed and doesn’t require major changes to an organization’s infrastructure. The ideal eCDN set-up for live video streaming for your organization is comprised of an ultra-low latency video encoder like the Haivision Makito X4, a scalable and flexible eCDN provider like Haivision Media Platform that can provide broadcast-quality video content to users, and any endpoint device such as a laptop, set top box, or mobile device to receive the organization’s streams and support P2P streaming.