Hitless failover (sometimes called hitless protection switching or seamless network switching,) increases the reliability of a live video stream by routing it over more than one network path. This prevents disruption to the live stream in the event of network congestion or failure.
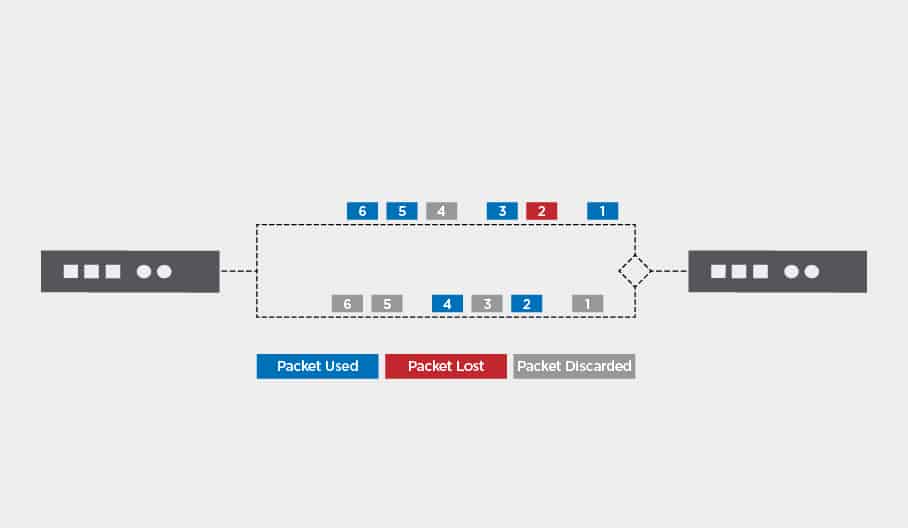
With hitless failover, a live stream is sent over two or more network paths simultaneously. Each network path can use its own combination of IP address and port number, or IP socket. Ideally each network path should be sent over separate NICs (network interface cards). This enables the identical streams to be routed over separate IP networks, typically two different ISPs.
Identical streams are sent over separate routes, but arrive at the same receiver. The receiver, typically a video decoder, will accept the first packet to arrive from either network path. If one network fails, interrupting the route, the receiver can then seamlessly switch to the other route. If a packet gets delayed or goes missing from one path the receiver can take it from another route. Hitless failover technologies such as Haivision Path Redundancy prevent packet loss and ensure uninterrupted video streaming.