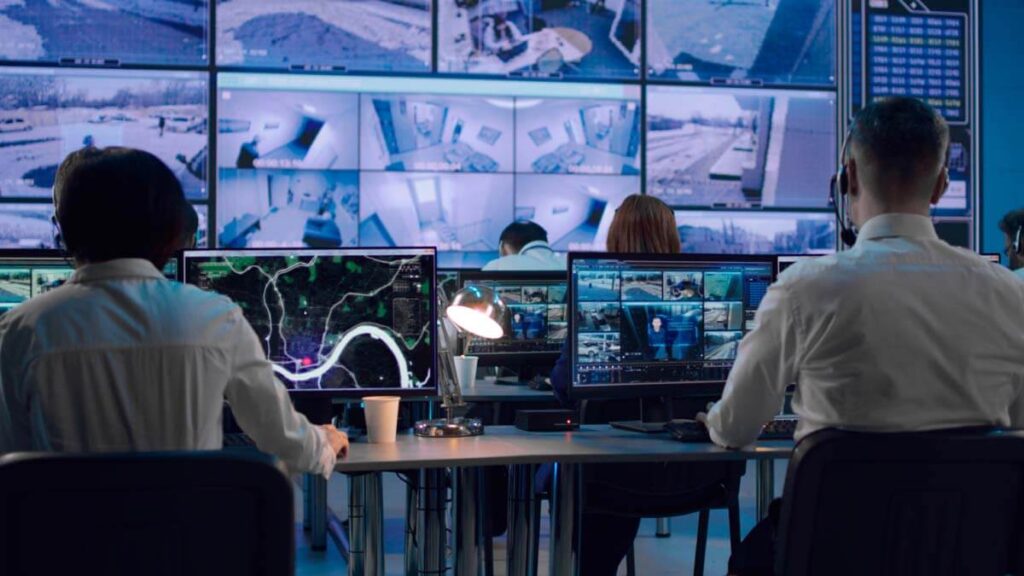
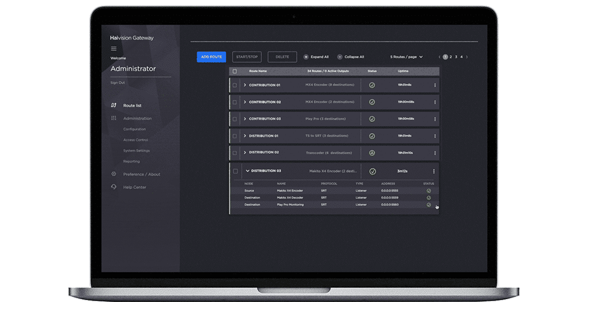
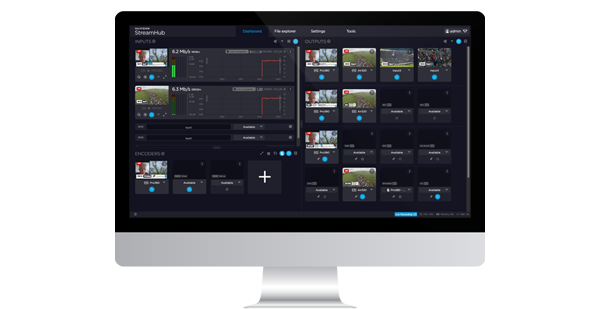
Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)

Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a data carrying technique for telecommunications networks. Specific to high-performance networks, MPLS uses short path labels to direct data from one network node to the next. By using this technique instead of long network addresses, this method avoids complex lookups in a routing table.
Traditionally, each router in a network would perform an independent IP lookup to determine the next-hop for data packets until the packets reach their final destination. With MPLS, the initial device still performs a routing lookup, but now finds a predetermined path to the final router.
The first device initiating the lookup then applies a label (or shim), to the data packet based on this information. Routers are then able to utilize that label to route traffic without the need for any additional IP lookups. And when the data reaches its destination, the label is removed and the packet is delivered through normal IP routing.
This data carrying technique can encapsulate packets of various network protocols and support a wide range of access technologies, including T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.
Latest Blog Articles